|
|

|

|
Speckle Reduction Imaging- SRI
|

|
HD Zoom
|

|
HD-Flow - “High Definition Flow”
|

|
Volume Contrast Imaging VCI-C
|

|
OmniView
|

|
Tomographic Ultrasound Imaging (TUI)
|

|
Inversion Mode
|

|
STIC – Spatio Temporal Image Correlation
|
|

|
|
|
|

|

|
"Retrocardiac Fluid Level in Chest X-Ray" at Tamil Nadu State Radiology & Imaging Conference at Jipmer Pondicherry on 9-10-83.
|

|
"A Case of Oesophageal Obstruction - Unusal Presentation" at Tamil Nadu State IMA Conference, Madras on 30-10-83.
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
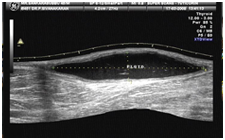
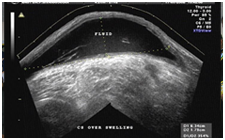
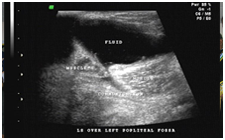
46 years old Male presented with history of swelling in left popliteal fossa noticed for the past 1 year. No significant pain or tenderness was present over the swelling. Ultra sound images (longitudinal and transverse extended views) over the popliteal fossa are given below.
|
|
|
|
Fig 1
|
Fig 2
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 3
|
|
The given images (Fig 1 & Fig 2) show fluid collection in superficial plane in
the popliteal fossa. The commonest cystic swelling in popliteal fossa is Baker’s
cyst, which is fluid collection within the synovial projection between
gastrocnemius and semimembranosus muscles. To diagnose Baker’s cyst
(gastrocnemius – semimembranosus bursa), we must demonstrate deeper
communication towards the capsule of the knee joint (Fig 3).
|
|
|
In the given images there is no deeper communication to suggest Bakers cyst. The
fluid collection is entirely confined to the superficial plane, which is
suggestive of lymph cyst. Lymph cyst usually results from a contusion in which
the skin is forcibly displaced from the subjacent tissues, and lymph vessels are
thereby torn across. The cyst is usually situated between the skin and fascia,
and contains clear or blood-stained serum. At first it is lax and fluctuates
readily, later it becomes larger and more tense.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|