|
An improved zoom factor allows for maintained image quality at an increased zoom level
|

|
High harmonics enables border/tissue differentiation
|

|
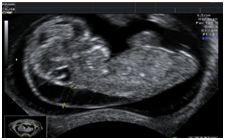
Combines the advantage of one overview image with one highly zoomed portion of it (e.g. fetal nuchal translucency measurement)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
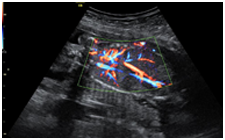
A broad band Doppler technique
Short broadband transmit pulses leads to improved axial resolution
|

|
Small sample volume reduces spatial overlap of clutter and tissue signals and thus improves sensitivity on small vessels
|

|
Improved sensitivity is gained through bandwidth matched RF processing
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
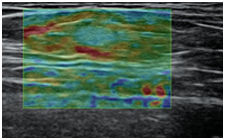
Ultrasound elastography is based on the comparison of ultrasound images, when the tissue is forcefully compressed. The principle behind ultrasound elastography is to characterize the soft biological tissues using the latest ultrasound technology to obtain a sequence of images which are processed for the ultrasound elastography Ultrasound elastography imaging performed during breast ultrasound is extremely helpful in evaluating breast lesions and selecting patients who need a biopsy, according to current research.
|
|
|
|
3D
|
|
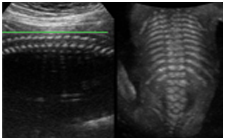
“Thick Slice” imaging utilizes volume ultrasound capabilities that renders
from slices in a volume.
|

|
Enhanced contrast and speckle suppression
|

|
Better assessment of size, margins & internal structures of lesions
|

|
Improved appearance of physiological structures
|

|
Enhances contrast thru compounding from different angles
|

|
Fewer artifacts (shadowing)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCI with selectable thickness, upto 3 planes simultaneously.
|

|
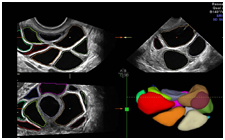
OmniView is the “Any-Plane” function for 3D and 4D data, either real-time or with reloaded cases
|

|
Images may be displayed as slice or VCI with selectable thickness (Competitive differentiator!)
|

|
OmniView allows to trace along any shape or structure
|
|
|
|
|
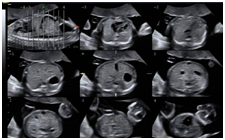
Make analysis and documenting of dynamic studies easier by providing a simultaneous view of multiple slices of a volume data set.
|

|
Top left held as reference image
|

|
Adjustable slice thickness
|

|
Selectable images for ease of documentation
|

|
Can combine with multiple features including STIC, SRI and CRI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Visualization of hypoechoic structures, which are difficult or impossible to display with conventional Ultrasound techniques.
|
|
Render algorithms analyze the target 3D Volume, displaying hypoechoic structures in a clear inverted surface rendered display, while simultaneously removing information from the surrounding tissue.
|
|
|
|
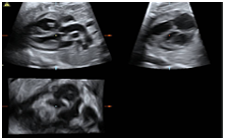
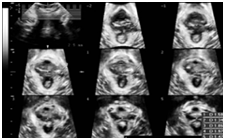
STIC allows quickly capturing a full fetal heart cycle beating in real-time and saving the volume for later analysis. Acquisition from 6-15 seconds
|

|
High image quality
|

|
Can combine with multiple features and rendering modes: TUI, B-Flow, Inversion, Glass Body and Minimum Mode
|

|
STIC provides a clinical solution for imaging the Fetal Heart
|
|
|
|
|

|
Possibility to change and select scan planes
|

|
Ability to post-process
|

|
Non-interventional – no external triggering required
|
|
|
|
Helps to display standard planes in fetal heart diagnosis.
Technology displays all the 2D planes, which complies with the recommended standard screening exam of the fetal heart, as outlined by AIUM, ACOG, ACR and ISOUG
|
|
|

|
Automated imaging tool that assists in displaying standard planes of fetal heart
|

|
Display all the 2D planes, which complies with the recommended standard screening exam of the fetal heart, as outlined by AIUM, ACOG, ACR and ISOUG
|

|
Image library added so that user can compare own image with reference image simultaneously on screen
|
|
|
Sonography-based Automated Volume Count follicle Improves the detection of hyperstimulated follicles
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Evaluation and visualization of any hypoechoic structure
Volume and Mean Diameter are calculated
|

|
Early Embryonic development (Gestational Sac Volume)
|

|
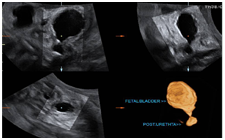
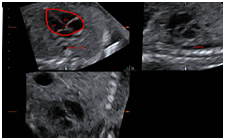
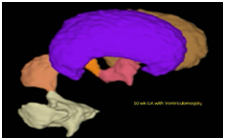
Fetal Brain Ventricles, Bladder, Stomach Visualization and Volume Calculation
|

|
Hydronephrosis
|

|
Cysts, Tumors & follow up
|

|
Any other hypoechogenic object
|
|
|
|
|
SonoAVC
|
Sonography-based Automated Volume Count
|
|
|
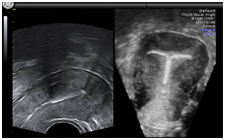
Pelvic floor imaging
|

|
Volume Ultrasound for transperineal scan of pelvic floor
|

|
Advanced 4D for Urethtra, Vagina, Rectum and Pubovisceral muscle
|

|
Ultrasound display of organs and muscles
|

|
Can identify damage to the Pelvic floor Muscle (Pubo rectalis)
|

|
Evaluation of stress incontinence
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|